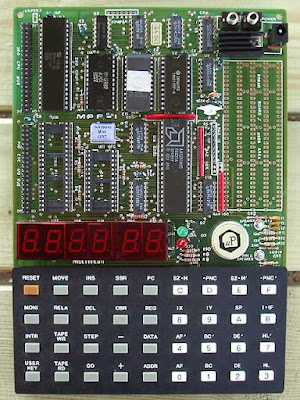
CSQ-600 troubleshooting failed :-(
I have been trying to troubleshoot a CSQ-600 received in very poor condition and obviously broken down for some time now. I found the few defective components and repaired the tracks interrupted by the backup battery acid. However, I can't get the machine to start. When I look at the signals from the processor on the oscilloscope, nothing happens.
So I assumed the CPU was down. I ordered a new component already programmed and saw the same type of behavior. In order to try to find out more, I mounted a tester of 8048 and 8748:
Using this assembly, I could see that reading both processors gave me the same memory dump, which bothers me a little since in fact, I can't find the beginning of a failure reason. So for fun, I passed the dump to the disassembler and got an ASM source.
Obviously, a quick look showed me that there was a problem:
In fact, this code can never be reached because there is a 'RET' before it and obviously no other part of the code points to 'inc @r0'.
I passed the dump in several disassemblers always obtaining the same result. From what I understand, neither the timer interrupt nor the INT interrupt are used in the CSQ-600 system. This is a program that runs continuously with reroutings depending on the positioning of certain flags including that of the INT input and that of the timer. The addresses concerned, 0x0003 and 0x0007 for IRQ & TIMER IRQ therefore do not contain a jump instruction.
I must say that with the simulator, some ports change their state at the rate of time elapsed by the timer. However, during my tests on the machine, I do not see any change in the state of the ports. So maybe it happens very quickly when the machine starts up (this is what I seem to have noticed with the logic analyzer), then afterwards, the processor goes into a loop and then nothing moves. Which does not tell me why the processor get into this state. I tried to change the state of the pins associated with a flag to see if that unblocked the situation but, again, nothing happened!
I passed the assembly code in a DOS simulator and as soon as I assembled, I did get an error:
This error is positioned on the line 'djnz r5,L02AC'. So I am not able to know if the generated ASM source is correct or maybe the memory dump is not correct. Since I don't have the original CSQ-600 processor binary file, after all my investigations I am unable to determine what the problem might be.
I'm not going to start disassembling the CSQ system by hand. So I decided to stop my investigations there. I will instead develop a small STM32 processor board which will replace the original processor. This will allow me to spend some 'pleasant time' operating the hardware parts of this machine and perhaps developing a complete system...
To be continued...
DRUMULATOR :
A few months ago, I bought a broken Drumulator. The objective was to use it to test the realization of the wave sequencer in FPGA:
The tests having been conclusive, I decided to completely reassemble the machine by fixing the various remaining problems. Once done, I realized that there was a power problem.
In fact, the regulator hidden under the black cover is defective. So I had to remove this component from the metal base of the Drumulator:
I discovered an SH323SC from Fairchild. On the other hand, I could see that the original regulator had therefore already been replaced. I decided to place an LT1083 that I have in stock.
Also, since the Drumulators Reset circuit is often a problem, I will implement my replacement board with auto-saved RAM. This will be more reliable than the original system.
It's quite incredible to see the 'shitty' tweaks that can sometimes be done on the machines. This Drumulator collected quite a few!
To be continued...
CNC:
A few days ago, I finally finalized the settings and operation of my little CNC. So I ordered and received the accessories needed to cut plastic and aluminum:
Obviously, when you don't know anything about it, you make order errors. It must be said that the explanations that can be found on the sites of certain retailers are, how to say, quite vague.
So I ordered two Collet Chucks suitable for a chuck much much larger than that of my CNC. Reference misinterpretation on my part. But hey, the second order was the right one :-)
I just have to find and test the software that will allow me to make the cuts I want to make. I have a feeling it won't be easy...
To be continued...